

Why are they done?
- To see if new treatments are safe and effective.
- To compare new and existing treatments.
Why might someone participate?
- To access the newest treatment with potentially better results or fewer side effects.
- To receive additional medical care during the trial.
- For those with no current treatment options, a clinical trial might be their only hope.
Remember, you should discuss participating in a clinical trial with your doctor before making a decision.
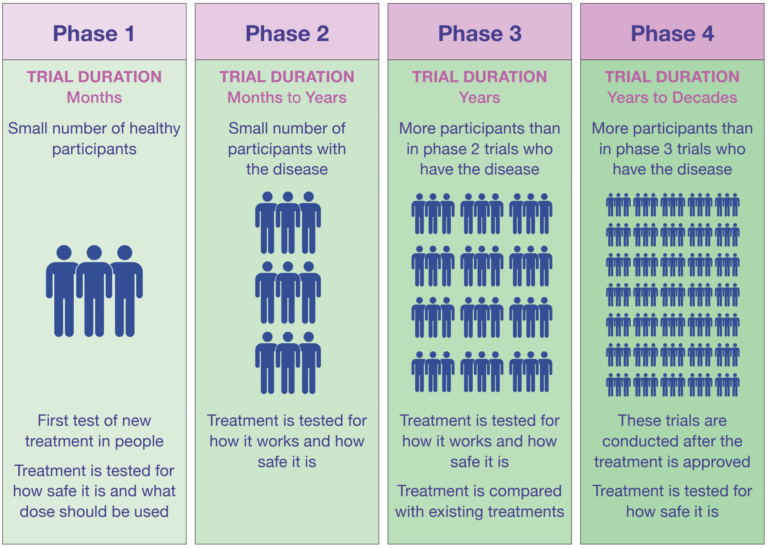
What are the differents initial stages called "Phases"?
- Before clinical trials: Treatments are first studied in a lab to ensure they function as intended.
- Clinical trial phases:
- Four main phases: Each phase tests the treatment in different ways with increasing numbers of participants.
- Combined phases for rare diseases: In some cases, phases might be combined or overlap.
- Importance of knowing the phase: Choosing a trial considers the phase, as each comes with specific benefits and risks.
You need to understand the importance of the trial phase when considering participating, as it influences potential risks and benefits.



What are two main options for the control group?
- Placebo: This is a substance with no active ingredient, designed to look like the new treatment. It helps researchers isolate the effects of the new treatment by eliminating the possibility of improvement due to other factors like the trial setting or participants’ expectations.
- Standard treatment: In some cases, researchers use the existing treatment for the disease as the control group. This allows them to compare the new treatment’s effectiveness directly to the current standard.
To ensure fairness and accurate comparisons, participants are often randomly assigned to receive either the new treatment, placebo, or standard treatment using a computer. In some trials, neither the participants nor the researchers know who received which treatment until the study ends (double-blind trials) to prevent bias influencing the results.
What to know before joining a trial?
Before joining a clinical trial, it’s crucial to understand the potential benefits, risks, and alternatives. The research team will thoroughly explain everything and provide you with informational materials to make an informed decision.
Here’s a summary of the key points:
- Understanding: You’ll receive detailed information about the trial, including potential benefits and risks, through explanations, materials, and opportunities to ask questions.
- Benefits: Participating could offer access to new treatments, additional medical care, or contributing to medical advancements.
You may have information and access to new support groups and resources. You help people to learn more about a disease
- Risks: These could include side effects from the new treatment, uncertainty about its effectiveness, and the burden of following trial procedures. You may not be part of the group that gets the new treatment but may instead be part of the group that gets a placebo or a standard treatment
- Alternatives: Evaluating alternatives to the trial, like existing treatment options, is crucial for making an informed choice.
- Medical team: Throughout the trial, a team of healthcare professionals will monitor your health, address side effects, and adjust treatment if necessary.



Participating in a Clinical Trial
Eligibility:
- Each trial aims to answer a specific research question.
- Inclusion criteria: Specific characteristics participants must have to be eligible.
- Exclusion criteria: Characteristics that disqualify someone from participating.
- You are eligible only if you meet all inclusion criteria and none of the exclusion criteria.
Informed Consent:
- Before participating, you must sign an informed consent form.
- This form details the trial’s:
- Purpose
- Duration
- Potential benefits and risks
- You have the right to:
- Review the form carefully at home.
- Discuss it with healthcare professionals and loved ones.
- Ask questions to the researchers.
- Signing the form confirms you understand the information and can choose to leave the trial at any time.
- The researchers may also remove you for health concerns.
Before Joining a Clinical Trial
Understanding the Trial:
- Before participating, thoroughly understand the specific trial you’re considering.
Risks and Benefits:
- Be aware that:
- New treatments involve uncertainties about effectiveness and potential side effects.
- Participation is voluntary and you can leave at any time, for any reason.
Financial Considerations:
- You should never pay for the trial treatment itself.
Qualified Professionals:
- Ensure the trial is led by healthcare professionals at a clinical site and monitored by an independent review board.
- Verify the qualifications and experience of the clinical trial staff.
Privacy:
- Clinical trial results may be published publicly, but participant identities are always protected.


DISCLAIMER
This brochure is for informational purposes only.
It does not provide medical advice nor encourage participation in any trial.
Always consult your doctor with any questions.
Please note that this information page was written by Syngap parents, not medical professionals.
It is based on the excellent work of SCN2A Asia Pacific. SCN2A Australia
More information here :
The Center for Information and Study on Clinical Research Participation:
information about clinical trials and search function for clinical trials
National Institutes of Health Clinical Research Trials and You:
information about clinical trials and how to find appropriate trials
https://www.nih.gov/health-information/nih-clinical-research-trials-you